How Many Watts Does It Take To Run A Refrigerator
Typically it takes about 350 watts to run a small refrigerator and about 780 watts to run a bigger refrigerator.
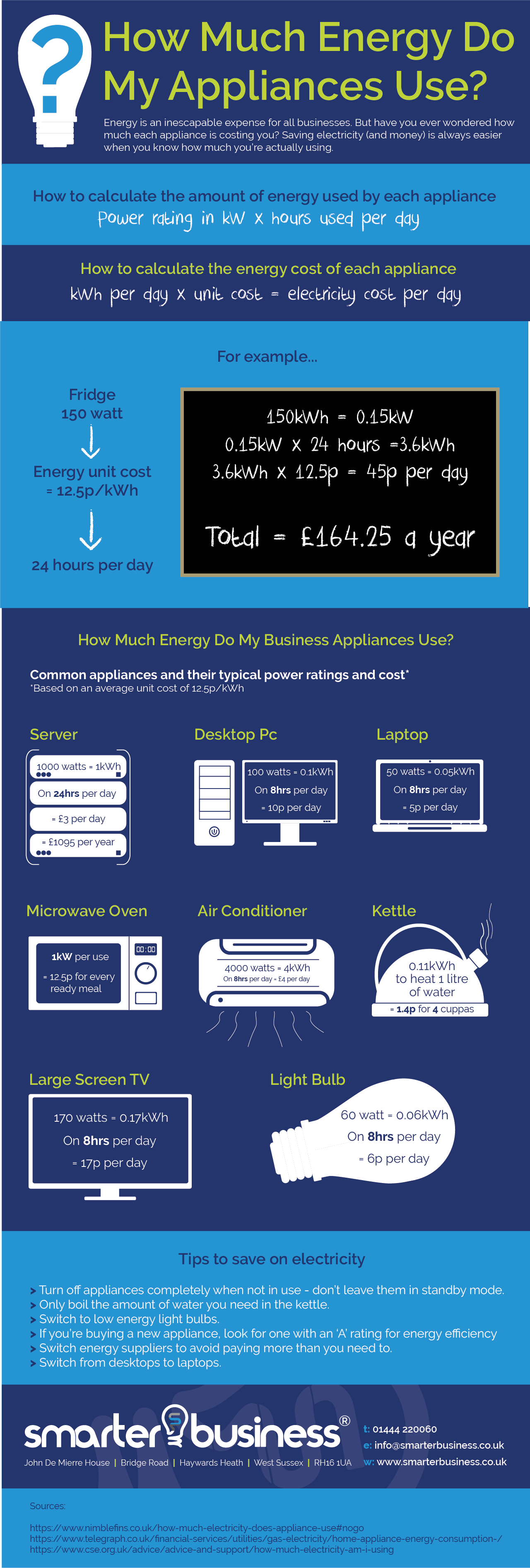
How many watts does it take to run a refrigerator. Divide by 24 and multiply by 1000 to get the watts. For most residential homes 200 will be more than enough with 180 watts being enough for fairly large fridges. So this fridge runs on about 46 running watts.
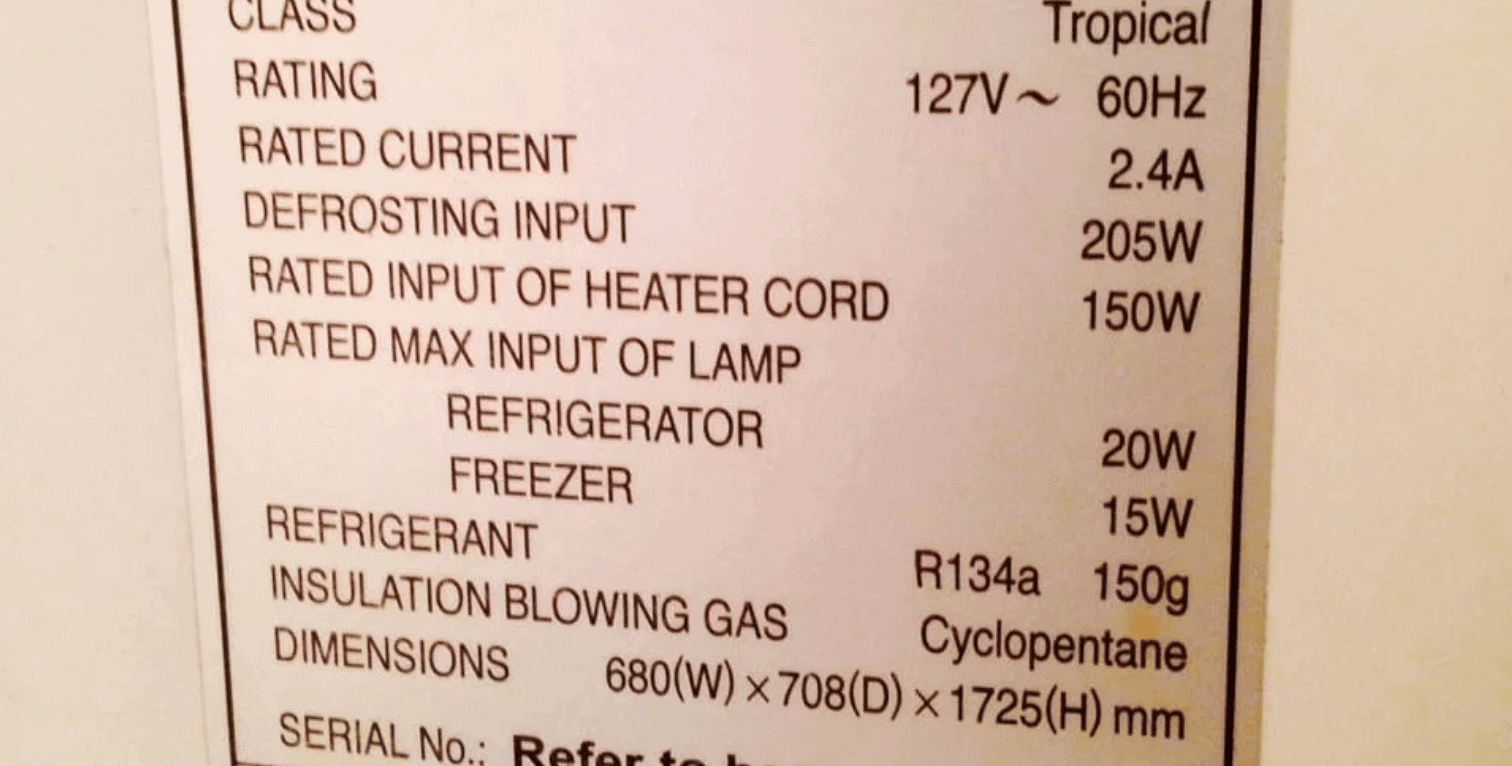
For example a class a refrigerator consumes approximately 100 watts per hour. Below is an example of the energy guide label you can find with your annual kwh usage. The most commonly used indicators are class and energy efficiency index.
If your refrigerator demands 780 watts multiply 780 by eight hours to get 6240 watts per day. If your utility charges 13 cents per kilowatt. A fridge freezer will of course require a bit more energy with a 240 liter combo requiring closer to 300 400.
The answer depends on the size of the fridge but the average refrigerator wattage ranges between 100 and 400 watts. The energyguide label that came with your fridge will typically list the fridges projected energy use per year in dollars. Typically minimum and maximum power levels are indicated.
The capacity of modern refrigerators ranges from 100 to 200 watts per hour. Refrigerators are reactive devices that require additional power to start because they contain an electric motor but significantly less watts to run as they remain on. Divide that by 365 to get 111kwh per day.
Conventional refrigerators typically have a starting wattage of 800 1200 watt hoursday and a running wattage of around 150 watt hoursday.